3 minutes
How BERT makes sense
English has many words with multiple meanings and they are often used in very different context.
The bank will not be accepting cash on Saturdays.
The river overflowed the bank
We humans can understand the context and relate the word with relevant meaning. This is a very basic requirement in natural language understanding. Let’s see how BERT, or contextual embedddings in general solve this problem, commonly know as word sense disambigution.
Word Sense Disambigution
Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) is the task to identify the correct sense of the usage of a word in a sentence. The solution to this problem impacts other computer-related writing, such as discourse, improving relevance of search engines etc. Various approaches, both supervised and semi-supervised methods, with the use of dictionaries have been introduced but the introduction of transformers made a significant impact like in almost all other NLP problems.
Deep Contextual Embeddings
Representing text as vectors is the core principle behind natural language processing. Earlier models like word2vec, GloVe, and FastText were used to used to train to get such representations. But the drawback of these representations is that they don’t aknowledge the disambiguity in meaning of words. Let’s go back to example mentioned above.
The bank will not be accepting cash on Saturdays.
The river overflowed the bank
In embeddings produced by word2vec like models, the word bank will be having same representation for both the sentences even though they have very different meaning. Also different words having different semantics will be having same representations.For example,in some sense, arrive and arrival, their semantics are almost the same, but they are different parts of speech: arrive is a verb and arrival is a noun, so they can appear in quite different places.Contextual embeddings solved these problems to an extent.
The concept of deep contextualized word embeddings was first introduced in ELMo.The main idea of the Embeddings from Language Models (ELMo) can be divided into two main tasks, first an LSTM-basedlanguage model is trained on a corpus and then the hidden embeddings are used to generate a vector representation for each word.
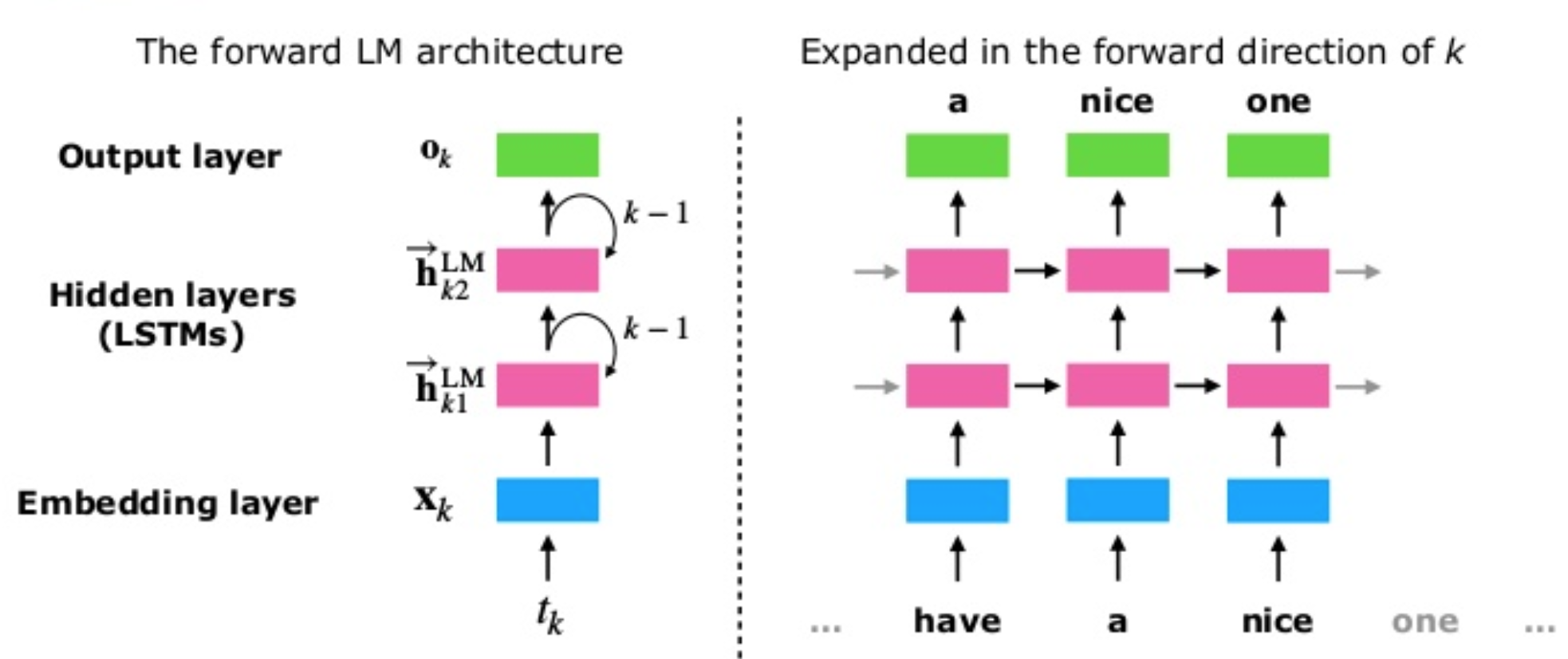
ELMos train a multi-layer, bi-directional, LSTM-based language model, and extract the hidden state of each layer for the input sequence of words. Then, they compute a weighted sum of those hidden states to obtain an embedding for each word. The weight of each hidden state is task-dependent and is learned during training of the end-task.
How does BERT do that?
Introduction of transformers revolutionised NLP domain. The Multi-layer bidirectional Transformer or Transformer was first introduced in the Attention is All You Need paper. It follows the encoder-decoder architecture of machine translation models, but it replaces the RNNs by a different network architecture. The key concept behind the effectiveness of transformers is Multi-Head Attention.
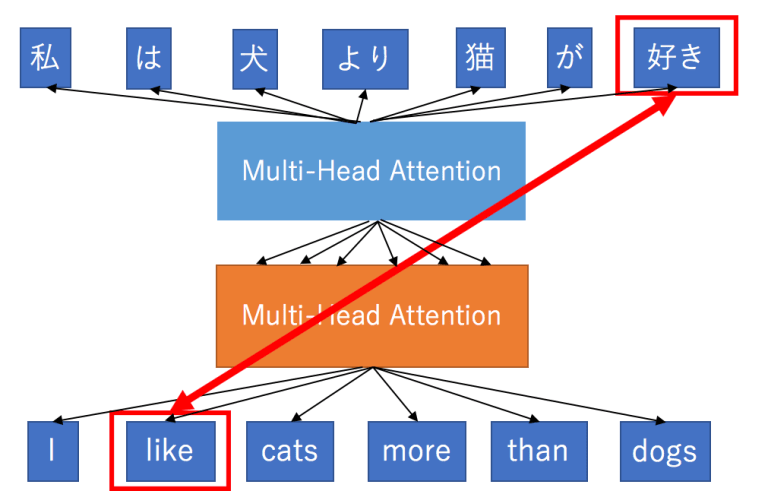
Several weighted sums are calculated for the same input using stacked multi-head attention models, with different linear transformations.
another factor is that, BERT is a non-directional model as it is trained by masking 15% of the words in a sentence and then making the model to learn by predicting the masked words using the information from the non-masked words.
All these factors help the contextual embeddings of bert to be efficient.